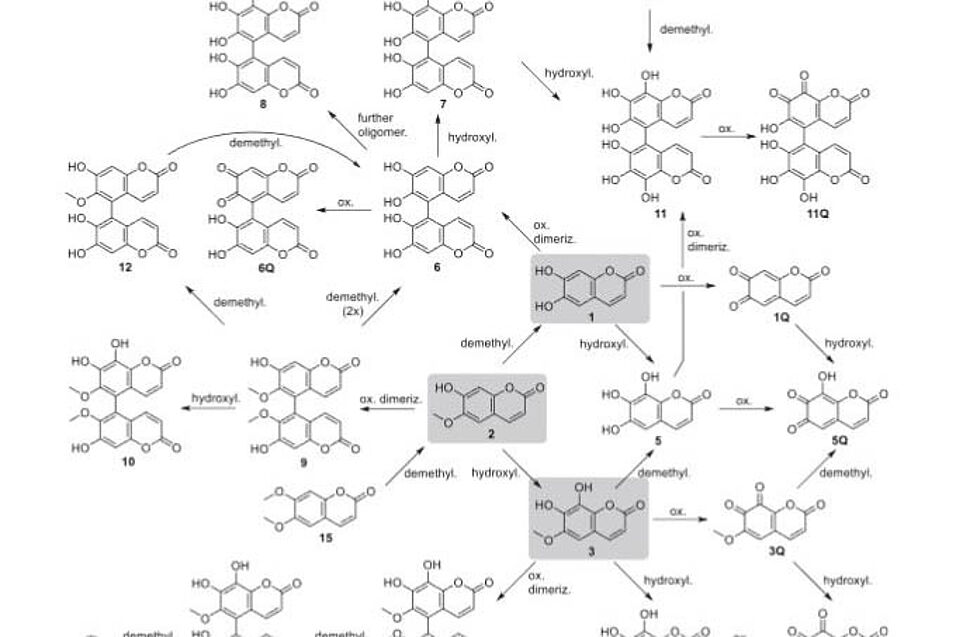
In order to verify this active role of oxidized coumarins in Fe(hydr)oxide dissolution, we complemented iron dissolution data with data of single coumarins (esculetin, scopoletin, fraxetin) and their oxidation products, as a function of time, pH, and mineral (goethite, lepidocrocite). Our results demonstrate that there are four different routes for coumarin oxidation, leading to quinones, dimers, hydroxylated coumarins, demethylated coumarins, and combinations of these. The time-dependent species pattern differs with respect to mineral, pH, and coumarin molecule. Oxidized coumarins are often more reactive than the original coumarins, explaining unexpected iron mobilization by scopoletin, which is demethylated to esculetin. Also oxidative hydroxylation and dimerization increase the number of phenolic groups and yield new chelating properties. Several iron-species are identified for the three coumarins. Since oxidation reactions are initiated directly at mineral surfaces, they are often very effective—but this does not always result in more iron mobilization.
New publication in Springer: Importance of oxidation products in coumarin-mediatedFe(hydr)oxide mineral dissolution