From Road to Plate (TireTox)

Tire wear particles form via mechanical and thermal abrasion of tires while driving, and collect on road surfaces. During rain events they are washed…
The impact of human activities on planetary systems is accelerating at an unprecedented rate. Natural and anthropogenic contaminants can drive systems outside safe operating spaces with far-reaching impacts on biodiversity, ecosystem services, and human health.
Our mission is to investigate the environmental fate and effects of organic and inorganic contaminants and processes at mineral interfaces. We train the next generation of leaders and societal actors.
Our vision is to inform solutions for the pressing environmental problems of today and tomorrow that sustain communities while stewarding the environment.

Tire wear particles form via mechanical and thermal abrasion of tires while driving, and collect on road surfaces. During rain events they are washed…

The input of anthropogenic chemicals into environmental systems is a major concern. For example, the presence of antibiotics in wastewater and…

Biopesticides are promising alternatives to synthetic pesticides – among other reasons also because they are expected to be biodegraded and thus of…

Given the wide gamut of issues cities are facing, the Research Platform "Urban Futures" focuses on five thematic areas: Society and Culture, Economy…

Long-term pollution mitigation requires a better understanding of the biogeochemical processes that regulate the behavior and fate of trace metals,…

The versatile applicability of plastics in our daily life lead to an increasing demand and production of plastics in the past decades and plastics…

The project investigates numerical approaches to bring forth best-management strategies crucial for drinking water production from bank filtration.…
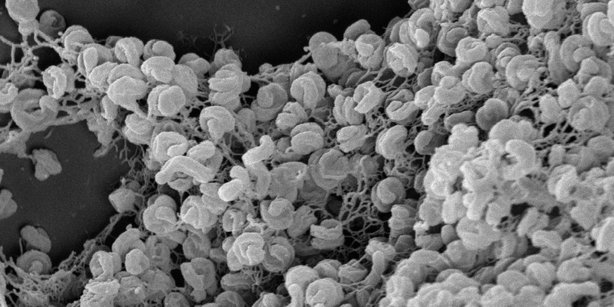
All organisms on Earth require certain types of trace metal co-factors like Fe, Mn and Cu for key enzymes in their metabolisms. Aerobic ammonia…

Aerobic methanotrophic bacteria oxidize the potent greenhouse gas methane (CH4) most efficiently via the copper (Cu)-bearing enzyme particulate…